Diabetic emergencies are diabetes-related health issues that sometimes require help from medical personnel. A diabetic emergency can be caused by too much insulin, too little insulin, or the wrong type of insulin; either naturally produced or as a medication.
If someone has a diabetic emergency, a few steps can be taken to manage blood sugar levels. Otherwise, they need to be taken immediately to an emergency room for treatment.
This article will focus on the three main diabetic emergencies and how to respond to them immediately.
What is Diabetes?
A healthy pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that allows glucose to enter cells and be used as fuel for energy production. When someone is diabetic they either don’t produce insulin or insulin isn’t used efficiently leading to raised levels of glucose in the blood. Blood sugar levels can be tested, leading to a diabetes diagnosis.
Type 1 diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder in which the person’s immune system attacks and destroys their own pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin so that insulin is no longer produced by the body. It needs to be controlled by taking insulin on a daily basis. There is currently no cure for type 1 diabetes, only forms of management.
Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes is due to insulin resistance and/or reduced insulin production by the pancreas. The vast majority of diabetics have type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes is a serious condition that can have serious consequences if not kept in check. If there isn’t enough insulin, either produced naturally or delivered through injections, glucose builds up in the bloodstream instead of going into cells where it’s needed and can lead to complications.
What is a Diabetic Emergency?
Diabetes has the potential to cause an emergency due to immediate excessive or deficient levels of blood glucose. Often times those situations can be managed by the person. Medical help should be sought when the person can’t help themselves (due to confusion, decreased motor skills, unconsciousness, etc.) or blood levels don’t return to normal.
Over time, uncontrolled blood sugar levels can lead to life-threatening complications such as heart attack, stroke, blindness, kidney damage, and limb amputation.
11 Reasons Why You Should DIY Your First Aid Kit
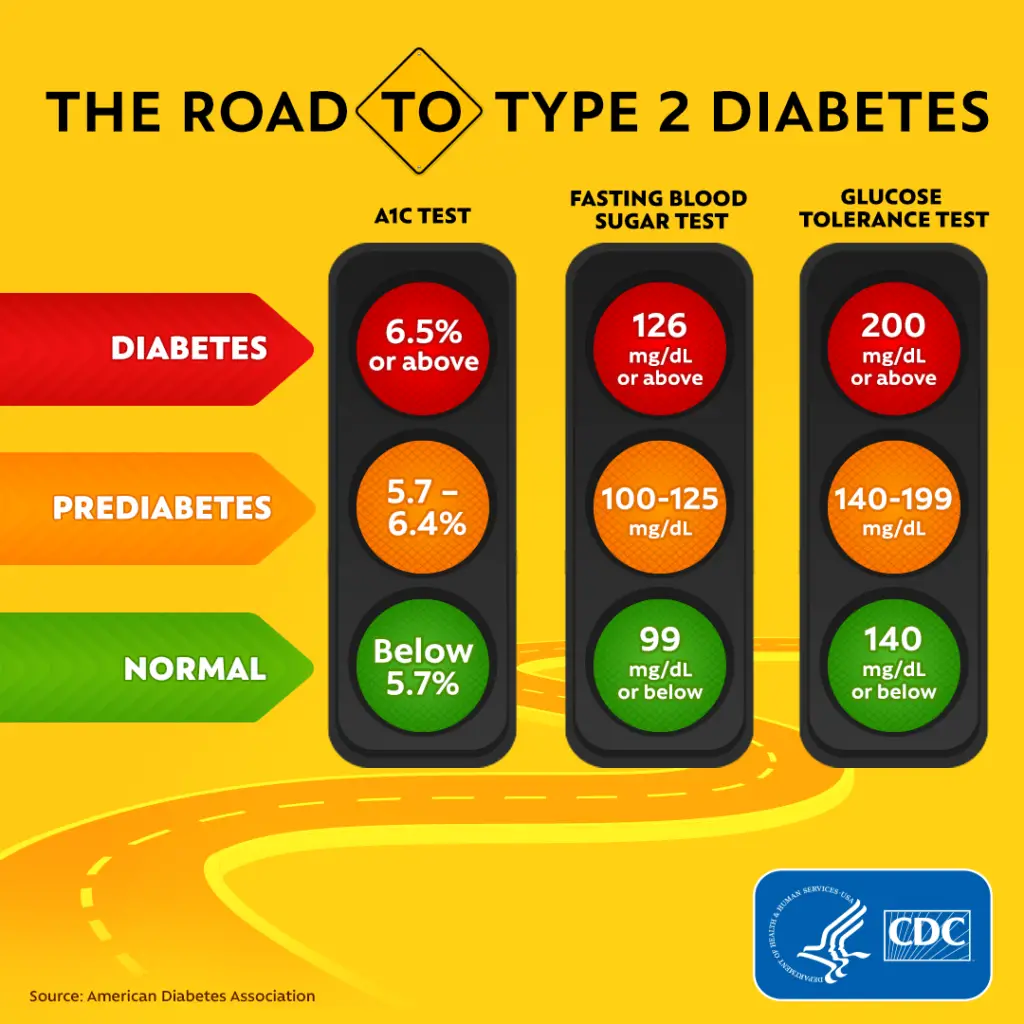
What are the three types of diabetic emergencies?
There are three main types of diabetic emergencies. They are hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), and ketoacidosis (DKA).
Hypoglycemia (Low Blood Sugar)
Low blood sugar is also called hypoglycemia. It is a condition in which the blood glucose level decreases below normal. Low blood sugar can be caused by eating too little food, eating food that does not have enough carbohydrates or it can happen if you are taking medications that lower your blood sugar.
Symptoms of Hypoglycemia
There are many symptoms of low blood sugar that could seemingly be associated with unrelated issues. The best way to tell if you have low blood sugar is to test your blood sugar levels. Some of the symptoms are listed below:
- Feeling tired and hungry
- Confusion
- Hunger
- Blurred Vision
- Having a headache or dizziness
- Irritability
- Feeling shaky or weak
- Having trouble concentrating or making decisions
- Coordination issues
- Sweating, increased heart rate, and anxiety
- Losing consciousness
The best way to be sure if you have low blood sugar is to test your blood sugar levels.
Preventing Hypoglycemia
Preventing hypoglycemia is all about managing glucose levels. In order to avoid hypoglycemia, a diabetic should keep a healthy diet and exercise routine. Checking one’s glucose levels often enough is also important in helping people avoid these side effects. You can also do the following:
- Don’t skip meals and eat at regular intervals
- If you are increasing your exercise duration and/or intensity, you may need to increase your caloric intake or adjust your medication.
- Limit your alcohol intake
- Monitor your blood sugar levels
How to Treat Hypoglycemia
The following measures should be taken to provide first aid and treat a diabetic for hypoglycemia:
- Sit the person down and have them relax.
- Give them something sweet and non-diluted such as juice and glucose tablets. These will increase their blood sugar level and help them recover quickly. Be sure not to give food too fast. The American Diabetes Association suggests the 15-15 rule: give 15 grams of carbohydrates and check after 15 minutes. Continue as needed.
- Monitor the person’s blood sugar level.
- If their condition continues to get worse or if conditions don’t stabilize after an hour, you should call 911.
People with diabetes should always keep things like sugar tablets, candy, juice boxes, or other emergency high-carbohydrate emergency foods.
Hyperglycemia (High Blood Sugar)
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which the blood sugar level in the body is higher than normal. This can be as a result of a lack of insulin in your body or your body resisting the effects of the insulin it has. Hyperglycemia causes many problems to the human body, ranging from dehydration to kidney failure to heart attack.
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
People with high blood sugar often experience thirst, frequent urination, excess hunger, blurred vision, drowsiness, and more. One of the most common symptoms is excessive urination. This is because the glucose that enters your bloodstream causes fluid to be pulled from your tissues into your bloodstream for use or storage. The excess fluid then passes out of your body through your urine. Some also experience blurred vision as a result of excess glucose in their bloodstreams forcing some fluids to move from the front part of their eyes to the back part where it’s less critical for visual acuity. There are also cases when people experience excessive hunger due to insulin resistance and ineffective absorption of glucose by cells lining the gastrointestinal tract (the small intestine).
Some of the common symptoms of high blood sugar include the following:
- Feeling excessively thirsty
- Feeling excessively hungry
- Urinating too often
- Headaches
- Blurred vision
- Fatigue
As you can see, several of these symptoms overlap with hypoglycemia. The best thing you can do is test your blood sugar levels to be sure they are above normal.
Preventing Hyperglycemia
The first step to preventing high blood sugar is to maintain a healthy weight. Additionally, eat a healthy diet and do not overeat. This will help keep your blood sugar levels in check. Next, you should exercise regularly. It could be as simple as going for a long walk or as intense as playing tennis every day. If you cannot commit to going for a walk every day, make sure that you do it as often as possible.
Steps to prevent high blood sugar:
- Don’t skip any doses of insulin or blood sugar medication.
- Make sure not to eat anything right before bedtime.
- Drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Eliminate or reduce alcohol consumption.
- You have an increased chance of getting high blood sugar if you are ill or stressed out.
- Check your blood sugar levels as often as suggested by your doctor.
How to Treat Hyperglycemia
The steps to treating hyperglycemia are as follows:
- Have the person stop eating and drink more fluids to bring their blood glucose down.
- Tell the person to check their urine for ketones – these are a sign that the body is breaking down fat instead of glucose for energy. If there are ketones in the urine, then let them know they need to go to an emergency room right away because they have diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). More info on testing here.
- If there are no ketones in the urine, then you can engage in physical activity to help metabolize some glucose. Simply going for a walk can be beneficial.
Ketoacidosis (DKA)
Ketoacidosis happens when the body cannot use glucose for energy due to a lack of insulin and instead uses fat for energy. Ketones are produced to break down the fat as an alternative energy source, thinking that there isn’t enough glucose available. This can happen during dieting, but for diabetics, this is a sign of an insulin imbalance that can be life-threatening. The liver will continue to produce ketones since glucose isn’t getting into the cells and poisons the blood. The condition can become very dangerous if left untreated. It is most common in people with type 1 diabetes.
Symptoms of Ketoacidosis
Here are some ways that you can determine if someone has reached this state:
- High blood sugar
- Ketones present in the urine
- Thirst / Dry mouth
- Excessive urination
- There may be nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain.
- The person may have a fruity smell on their breath.
- Confusion
- Flushed skin
- In the most severe cases, it will cause a diabetic coma or death.
Preventing Ketoacidosis
People with diabetes should take extra precautions to prevent Ketoacidosis, although it is rare in people with type 2 diabetes. Many of the ways you would prevent it are the same as how to prevent high blood sugar. Some ways to help prevent ketoacidosis are:
- Ensure that the proper amount of insulin was taken, or that a dose wasn’t missed altogether.
- Don’t miss any meals and ensure you are eating enough healthy foods.
- Maintain your exercise routine.
- Know that when you are stressed or sick, there is an increased likelihood of ketoacidosis.
How to Treat Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a serious condition and should be addressed by medical personnel. What you can do in the meantime is drink plenty of fluids with electrolytes. Once at the hospital, you will likely receive insulin therapy and fluids through an IV until your blood sugar levels out.
How to Test for Ketones
Testing is the best way to determine if a person has ketoacidosis. The two most common ways of testing for ketones are:
Urine Ketone Testing: This is one of the most common ways to test for ketones, but it is less accurate than blood testing. You can buy test strips from any pharmacy or online to use at home.
Blood Ketone Testing: The most accurate way to detect ketones is through a blood test. This can reveal whether you are experiencing diabetic ketoacidosis.
How to Monitor Blood Sugar Levels for Diabetics
It is important for diabetics to monitor their blood sugar levels. Over time, you’ll be able to see your progress and learn how your exercise and diet affect your blood sugar. The following are different methods of monitoring blood sugar levels.
One way is to use a continuous glucose monitor which is inserted under the skin. This device sends information about the person’s glucose level to a receiver that displays the reading on a screen or to the person’s cell phone. If their blood sugar is too high or too low, they will receive a warning from the device or phone app.
Another way is to track your blood glucose with a glucometer and test strips. The person’s finger is pricked and a drop of blood is placed on the test strip. It will then react chemically with the strip and give you your reading.
Follow your doctor’s recommendations on how often to monitor your blood sugar levels.
Final Thoughts
- Diabetes is different for everyone. Be sure to discuss anything out of the ordinary with your doctor.
- The best way to help people that are having a diabetic emergency is to know the signs and symptoms.
- If you are diabetic, carry some form of diabetic identification like a bracelet or ID card.
- If the person is taking insulin or other medications, be sure they are following the proper dosage and schedule. The amount of insulin you need can change over time.
- Diabetics, especially those prone to low blood sugar, should keep emergency foods or glucose pills on hand in case of hypoglycemia.
- Proper diet and regular exercise is the best way to manage diabetes beyond taking the required medication.
Sources:
www.diabetes.org
www.mayoclinic.com
www.webmd.com
Are you living with diabetes? We’d like to hear your thoughts in the comments below.